 International Desk: Addition of enzymes to monogastric diets is a widely used practice in the feed industry to improve digestion of difficult to digest components present in those diets, thereby enhancing production performance, and reducing feed cost per unit of animal product.
International Desk: Addition of enzymes to monogastric diets is a widely used practice in the feed industry to improve digestion of difficult to digest components present in those diets, thereby enhancing production performance, and reducing feed cost per unit of animal product.
Xylanase is one of the enzymes used to break down a part of the non-starch polysaccharide fraction. In many countries where monogastric diets are mostly corn-soybean meal based, the use of xylanases is often associated with limited periods of time during which wheat is used. This is because some still believe that a xylanase is only used to reduce the viscosity of the diet, and to improve wheat digestibility and litter quality. Once those periods of wheat use pass, and corn becomes available or cheaper, the use of xylanases is often abandoned or seen as a secondary activity at best. What is often forgotten, is that corn, and many other vegetable raw materials, also contain significant amounts of arabinoxylan (AX), the substrate for xylanase.
Arabinoxylans
Arabinoxylan, a non-starch polysaccharide (NSP) and poorly digestible plant cell wall component, is by far the most important anti-nutritional carbohydrate fraction in raw materials, as is also the case in corn. Due to its abundance, its location in the plant material and the lack of endogenous NSP enzyme production in monogastrics, AX reduces feed digestibility and therefore animal performance considerably. However, the arabinoxylan fraction in corn, as in all other vegetable raw materials, is largely insoluble and difficult to degrade. This imposes different requirements to a xylanase in order to have beneficial effects in corn-soy based diets.
Due to its enzyme-resistant properties, the water-insoluble AX fraction is much more difficult to degrade than the water-soluble fraction. For this reason, most xylanases have failed to bring big improvements to corn-soy diets because they fail to degrade the water-insoluble AX fraction. This has led to much disappointment among nutritionists with regard to xylanase efficacy in corn-soy diets.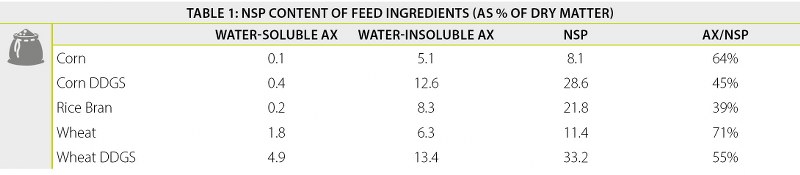
Furthermore, many are simply not aware of the fact that the high amounts of insoluble AX present in corn, rice bran and other raw materials alike, offers a unique potential for enzyme-mediated in vivo production of prebiotic oligosaccharides. The partial hydrolysis of soluble and insoluble AX into smaller arabinoxylan oligosaccharides (AXOS) makes them an ideal substrate for fermentation by beneficial microbiota. In turn, this results in the production of important levels of desirable SCFAs in the GIT, particularly butyrate. Butyrate supports the intestinal integrity and the development of beneficial microbiota, improves gut morphology and modulates the immune system.
Nutrase Xyla HS
Nutrase Xyla HS is a unique endo-xylanase able to break down both water-soluble and water-insoluble AX. Moreover, Nutrase Xyla HS has been found to be superior to other xylanases with regards to the breakdown of the water-insoluble AX fraction. Hydrolysis of the soluble AX fraction is important in high viscosity diets, such as those containing high amounts of wheat. However, the degradation of water-insoluble AX is important in all types of cereal-based diets. Not only does it result in the release of additional energy and nutrients, but the in vivo production of prebiotic AXOS fragments has been shown to stimulate butyrate production inside the digestive tract. Thanks to its optimal activity at neutral pH, Nutrase Xyla HS has a longer time to work at its maximum capacity in the gastro-intestinal tract compared to other xylanases. Furthermore, Nutrase Xyla HS is highly stable and can withstand intensive and high temperature pelleting conditions.
To verify and validate the effects of Nutrase Xyla HS, a broiler trial was conducted in close cooperation with the research facility of AgriVet Consultancy Pvt Ltd. in India. In a floor pen trial, Cobb 430Y male broilers were reared for 42 days. The broilers were allocated to 3 treatments (Table 2) with 6 replicates per treatment. For all animals, a three phase dietary program (starter d0-14, grower d15-28 and finisher d29-42) was used in which all diets (composition in Table 3) were fed ad libitum. Body weight and feed intake were recorded at weekly intervals, and pen mortality was recorded to correct feed intake. Additionally, at day 42, 1 bird per pen was euthanized to collect the intestinal content of the jejunum and ileum to measure the impact of the various treatments on digesta viscosity.
Results
Supplementation of Nutrase Xyla HS to the diet resulted in a substantial positive effect on feed conversion, leading to a 5-point improvement in corrected feed conversion (FCc) compared to the positive control group, and 4 points compared to the negative control group. In this trial, no significant differences were observed on the final body weight.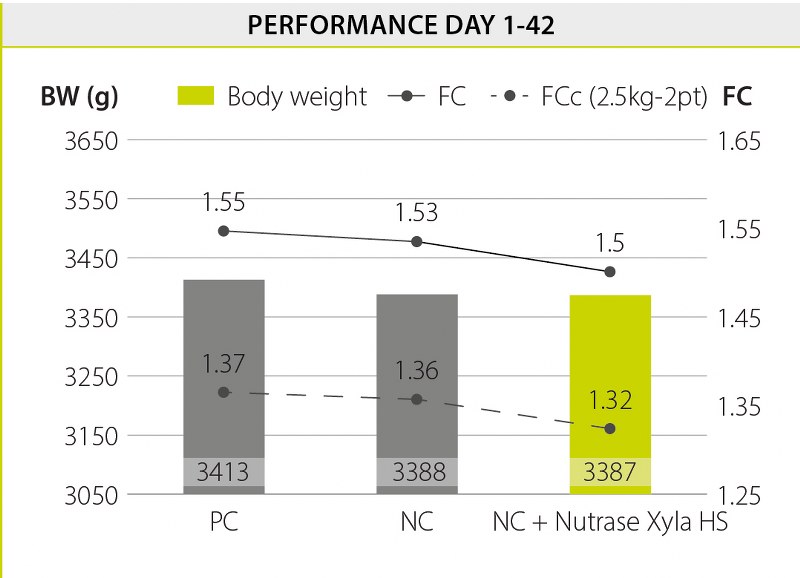
Although the diet did not contain any high viscosity ingredients, supplementation of Nutrase Xyla HS to diet also resulted in a clearly reduced intestinal viscosity compared to both control diets, thereby improving digestion and litter quality.
Conclusion
Supplementation with Nutrase Xyla HS improves intestinal viscosity and feed conversion of broilers fed diets with reduced energy levels. Based on these trial results, Nutrase Xyla HS can be supplemented to a corn-based diet with matrix values of 100 kcal AME without detrimental effect on broiler performance. Thanks to its unique set of properties, Nutrase Xyla HS can thus substantially reduce feed costs while maintaining performance.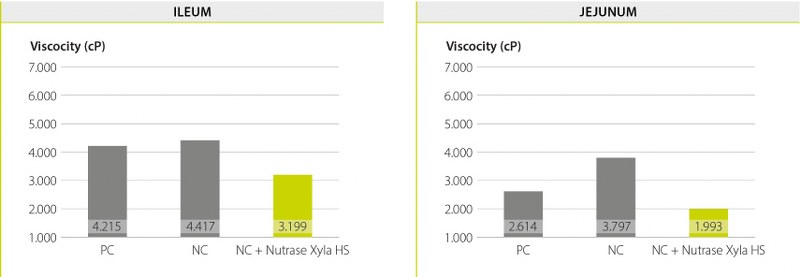
Nutrase Xyla HS has a proven record of efficiently breaking down water-insoluble AX, making it especially successful in corn based diets. Furthermore, Nutrase Xyla HS also impacts intestinal health through the indirect prebiotic action. The combination of Nutrase Xyla HS characteristics strongly boosts monogastric performance and reduces production costs, regardless if they are fed a corn, wheat or other cereal based diet.
Nutrex
Nutrase Xyla HS is a unique product from Nutrex, a leading supplier of innovative, top quality feed additives, with headquarters in Belgium and an expansive distribution network across the world. Nutrex products are developed in close cooperation with leading research institutes and universities and marketed based on solid research. Nutrex prides itself in providing the finishing touch for nutrition by consistently high value to its customers’ products, allowing them to save more costs and improve performance.
Authors : Jesse Stoops, PhD & Kurt Van de Mierop MSc –Nutrex nv
 Agrinews24 কৃষির সাথে, কৃষকের পাশে
Agrinews24 কৃষির সাথে, কৃষকের পাশে





















